

It will, nonetheless, still contain significant quantities of the valuable isotope, so it is not simply thrown away. The other part of the output of the first stage will, of course, be slightly depleted in U-235. Such a collection of centrifuges is called a cascade and any given set of centrifuges operating in parallel is called a stage. Each set of centrifuges enriches the uranium a bit more than the previous until the desired enrichment is achieved. To get the necessary degree of enrichment, the enriched output of one set of centrifuges will be fed in as input to another set of centrifuges for further enrichment. To process sufficient material, centrifuges, sometimes hundreds, are operated in parallel. No single centrifuge can achieve an adequate degree of enrichment and the amount of material that a single centrifuge can handle is small. From one end the gas will be slightly enriched in U-235 compared to the feed gas and at the opposite end the gas will be slightly depleted in U-235 compared to the feed gas. Tubes running along the center of the rotor extract the UF6 gas. This is one reason that the longer the rotor, the greater the separation of the centrifuge. Thus, the U-235 and U-238 do not separate relative to the wall and the center but along the length of the centrifuge. The U-235 will spend, on average, more time being pushed along with the flow along the center and will concentrate at the opposite end.

Being more often near the wall, the U-238 will get pushed along with the wall flow in the direction of the hot or scoop end of the rotor more often than it will get pushed along the center flow, thereby increasing its concentration at that end. To say that the concentration of U-238 is higher along the wall and U-235 higher along the center, simply means that, statistically, each molecule containing 238 will spend more time on average along the wall than a molecule containing U-235, which will, statistically, spend a relatively longer time near the center.
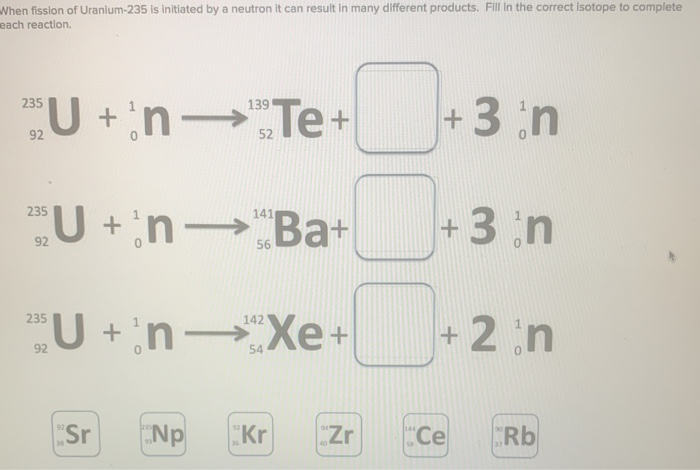
To be useful, the concentration of U-235 must be increased to 3-5 percent for a typical commercial reactor and to 80-95 percent for a nuclear weapon.Īs in any gas, the molecules of UF 6 are not static, rather individual molecules have thermal energy and are moving around within the volume of gas. (Thus, materials like U-235 and plutonium are called “fissionable”.) The U-238 is not directly fissionable. It is the U-235 that can be directly split, or fissioned, to produce power in most of the world’s current commercial nuclear reactors. Such is the case with uranium, which is made up of two isotopes, the predominant uranium-238 (or U-238) and U-235, which is only 0.7% of natural uranium. While the chemical properties of two isotopes are almost identical, the difference in the number of neutrons in the nucleus can result in nuclear properties that are dramatically different. Most chemical elements have different isotopes, which are atoms with slightly different weights resulting from the different number of neutrons in the nucleus.
However, uranium cannot be used in its natural form– it must be processed to increase the concentration of the active isotope of uranium, U-235. Uranium powers both nuclear reactors and nuclear bombs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
